We post here the relevant reports for the power sector in Nigeria. Feel free to join our efforts and share us any other you may have found. We'd be glad to add them to the list. Just send an email to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Publication date: 2016, June
Author: African Research Review
Description: The power sector in Nigeria through the years have been a tortuous, difficult, painful, devastating and herculean task for both the governments and the populace. A population of about 170 million people with more than half of them living without electric power supply, certainly presents a catastrophic situation for economic and social development of the nation and the people. Consequently, this paper tries to analyze the implications of the reforms propounded by law and policy, the extent to which the said reforms have improved or otherwise aided the power sector in supplying of electricity, the challenges with generation, distribution and transmission, the capacity which the sector can produce to serve the entire Nigerians etc. This paper furthermore made recommendations on how the Nigerian power sector can be reformed through the application of law and its overall benefits to the economic, social and national development of the country and the populace.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2016, June
Author: africapractice
Description: The downturn in global oil prices has placed significant pressure on Nigeria's economy, turning the spotlight on a number of structural, legal and political issues underpinning the country's energy sector. Last year's landmark change in government has brought renewed impetus to energy sector reform initiatives. However, President Muhammadu Buhari's administration faces many of the same challenges as his predecessors in advancing the reform agenda. In this note, we explore what we believe to be five of the most critical issues affecting the strategic outlook for the country's energy sector across the length of its value chain.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2016, February
Author: Latham & Watkins
Description: A summary of the existing power sector in Nigeria, current key initiatives, and opportunities and challenges for developers, investors and lenders.
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2016
Author: Springer
Description: The chapter presents the status quo of Nigeria’s energy sector and is divided into five sections. The first extensively reviews the various conventional and renewable energy resources in Nigeria. The second and third sections presents the primary energy supply and consumption, respectively. The forth section presents an insight into the various government ministries, parastatals, and agencies that are relevant in the Nigerian energy sector. The last section in this chapter explores the Nigerian energy policies and strategies.
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2016
Author: Energy Access for All
Description: Despite Nigeria’s abundance of fossil and renewable energy resources, Nigerians still experience acute energy poverty: they either lack access to modern energy sources or have to cope with inadequate supply and poor quality. Close to 95 million people are fully reliant on traditional wood stoves for cooking, with the attendant health implications,i and a large but unknown number of especially urban households rely on generators for their electricity needs.
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2016
Author: Universiti Tenaga Nasional
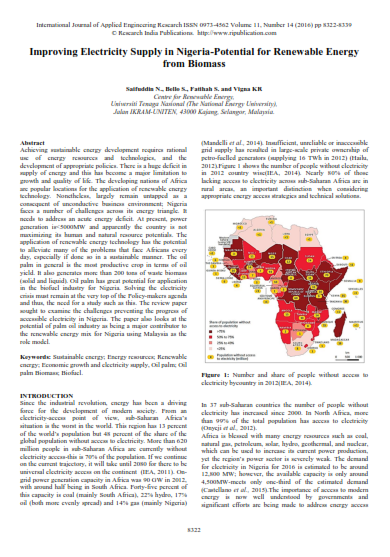
Description: Achieving sustainable energy development requires rational use of energy resources and technologies, and the development of appropriate policies. There is a huge deficit in supply of energy and this has become a major limitation to growth and quality of life. The developing nations of Africa are popular locations for the application of renewable energy technology. Nonetheless, largely remain untapped as a consequent of unconductive business environment; Nigeria faces a number of challenges across its energy triangle.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2016
Author: NERC
Description: In exercise of the powers to make regulations conferred by Sections 96(1) and 70(8) of the Electric Power Sector Reform Act 2005 (Act No.6 of 2005) and all other powers enabling it, the Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission makes the following Regulations for Mini-Grids.
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2016
Author: Power Africa
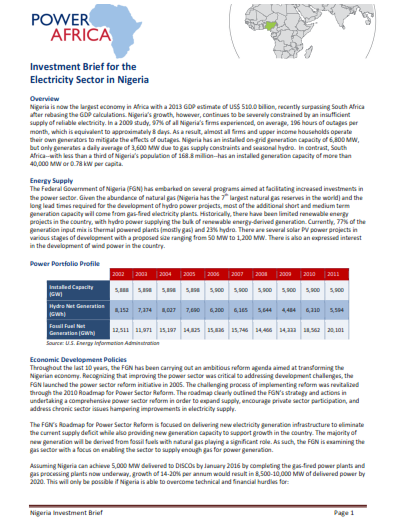
Description: Nigeria is the largest economy in sub-Saharan Africa, but limitations in the power sector constrain growth. Nigeria is endowed with large oil, gas, hydro and solar resource, and it already has the potential to generate 12,522 megawatts (MW) of electric power from existing plants, but most days is only able to generate around 4,000 MW, which is insufficient. Nigeria has privatized its distribution companies, so there is a wide range of tariffs.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2015, August
Author: Ministry of Energy
Description: Country Report on Nigeria Energy System.
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2015, August
Author: Advocaat
Description: One of the key objectives of the Nigeria Electricity Sector reform was to create efficient market structures, within clear regulatory frameworks, that would encourage competitive markets for the entire electricity value chain in Nigeria. The implementation of market competition in the electricity sector was designed to progress gradually in four phases- the Pre-Transition Electricity Market (Pre-TEM), the Transition Electricity Market (TEM), Medium Term Electricity Market (MTEM) and the Long Term Electricity Market (LTEM).
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2015, June
Author: Energy Commission of Nigeria
Description: The National Energy Summit is to provide fora for discourse on the Nigerian energy sector in order to facilitate the monitoring of the performance of the energy sector in the execution of government policies on energy.
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2015, June
Author: EU / GIZ
Description: On behalf of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) and with co-financing by the European Union (EU), the Nigerian Energy Support Programme (NESP) is supporting the Nigerian Federal Ministry of Power, Works and Housing and other public and private partners to improve access to sustainable energy.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2015, April
Author: Federal Ministry of Power
Description: Energy supply in Nigeria can be classified into two main categories, (a) urban and (b) rural. Urban areas are essentially on the grid while rural areas are largely off the grid. Improved energy supply to urban residents is being addressed mainly by the Roadmap for Power Sector Reforms, which was launched by President Goodluck Ebele Jonathan, GCFR, in August 2012. The roadmap essentially focuses on the development of grid-based electricity. However, the on-going power sector reforms will only enable the extension of the national grid to large rural areas which are close to main urban areas.
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2015, March
Author: Power Africa
Description: Nigeria is the largest economy in sub-Saharan Africa, but limitations in the power sector constrain growth. Nigeria is endowed with large oil, gas, hydro and solar resource, and it already has the potential to generate 12,522 megawatts (MW) of electric power from existing plants, but most days is only able to generate around 4,000 MW, which is insufficient. Nigeria has privatized its distribution companies, so there is a wide range of tariffs.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2015, March
Author: Springer
Description: This paper provides the foundation for the Nigerian Rural Electrification Agency (NREA) to develop an electrification plan as well as involve all stakeholders in carrying out direct surveys towards generating a database for rural electrification status in Nigeria.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2015, March
Author: Energy Commission of Nigeria
Description: Proceedings of the Summit on Energy and the Transformation Agenda in Nigeria.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2015, March
Author: Energy Commission of Nigeria
Description: Nigeria Energy Calculator 2050 (NECAL2050).
Download Report >>
Publication date: 2015, March
Author: Energy Commission of Nigeria
Description: Energy Efficiency as a Driver for Economic Transformation and Sustainable Development.
Publication date: 2015
Author: AJUMOGOBIA & OKEKE
Description: Nigeria has made a major transition from a vertically integrated, publicly-owned electricity network to a largely privately-owned unbundled electricity network, with the separation of the different segments of electricity business through a process called ‘unbundling’. The reforms have moved Nigerian power sector from a state monopoly to a competitive electricity market. Prior to the 2005 reforms, Nigeria, with a population of 165 million people, and an average generation of about 3,800 megawatts (MW), had a low per capita consumption. Thus, Nigeria embarked on the liberalisation and privatisation of electricity sector.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>
Publication date: 2014, October
Author: Covenant University
Description: The history of electricity development in Nigeria can be traced back to the end of the 19th Century, when the first generating power plant was installed in Marina, Lagos, in 1898, fifteen years after its introduction in England. Its total capacity was 60kW.
Download Report >>
Visit Website >>